
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Zhejiang Laboratory, Research Center for Frontier Fundamental Studies, Hangzhou, China
2 Zhejiang University, College of Optical Science and Engineering, State Key Laboratory of Extreme Photonics and Instrumentation, Hangzhou, China
3 ZJU-Hangzhou Global Scientific and Technological Innovation Center, Hangzhou, China
4 Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Chip Hub for Integrated Photonics Xplore (CHIPX), Wuxi, China
With the rapid development of sensor networks, machine vision faces the problem of storing and computing massive data. The human visual system has a very efficient information sense and computation ability, which has enlightening significance for solving the above problems in machine vision. This review aims to comprehensively summarize the latest advances in bio-inspired image sensors that can be used to improve machine-vision processing efficiency. After briefly introducing the research background, the relevant mechanisms of visual information processing in human visual systems are briefly discussed, including layer-by-layer processing, sparse coding, and neural adaptation. Subsequently, the cases and performance of image sensors corresponding to various bio-inspired mechanisms are introduced. Finally, the challenges and perspectives of implementing bio-inspired image sensors for efficient machine vision are discussed.
bio-inspired image sensor machine vision layer-by-layer processing sparse coding neural adaptation Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(2): 024001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Research Center for Humanoid Sensing, Zhejiang Lab, Hangzhou 311121, China
2 ZJU-Hangzhou Global Scientific and Technological Innovation Center, Hangzhou 310014, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, International Research Center for Advanced Photonics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
Miniaturized fiber-Bragg-grating (FBG) interrogators are of interest for applications in the areas where weight and size controlling is important, e.g., airplanes and aerospace or in-situ monitoring. An ultra-compact high-precision on-chip interrogator is proposed based on a tailored arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) platform. The on-chip interrogator enables continuous wavelength interrogation from 1 544 nm to 1 568 nm with the wavelength accuracy of less than 1 pm [the root-mean-square error (RMSE) is 0.73 pm] over the whole wavelength range. The chip loss is less than 5 dB. The 1 × 16 AWG is optimized to achieve a large bandwidth and a low noise level at each channel, and the FBG reflection peaks can be detected by multiple output channels of the AWG. The fabricated AWG is utilized to interrogate FBG sensors through the center of gravity (CoG) algorithm. The validation of an on-chip FBG interrogator that works with sub-picometer wavelength accuracy in a broad wavelength range shows large potential for applications in miniaturized fiber optic sensing systems.
Fiber optic sensing on-chip interrogator arrayed waveguide grating center of gravity Photonic Sensors
2024, 14(1): 240126
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Zhejiang Lab, Research Center for Humanoid Sensing, Hangzhou, China
2 Zhejiang University, College of Optical Science and Engineering, International Research Center for Advanced Photonics, State Key Laboratory of Extreme Photonics and Instrumentation, Hangzhou, China
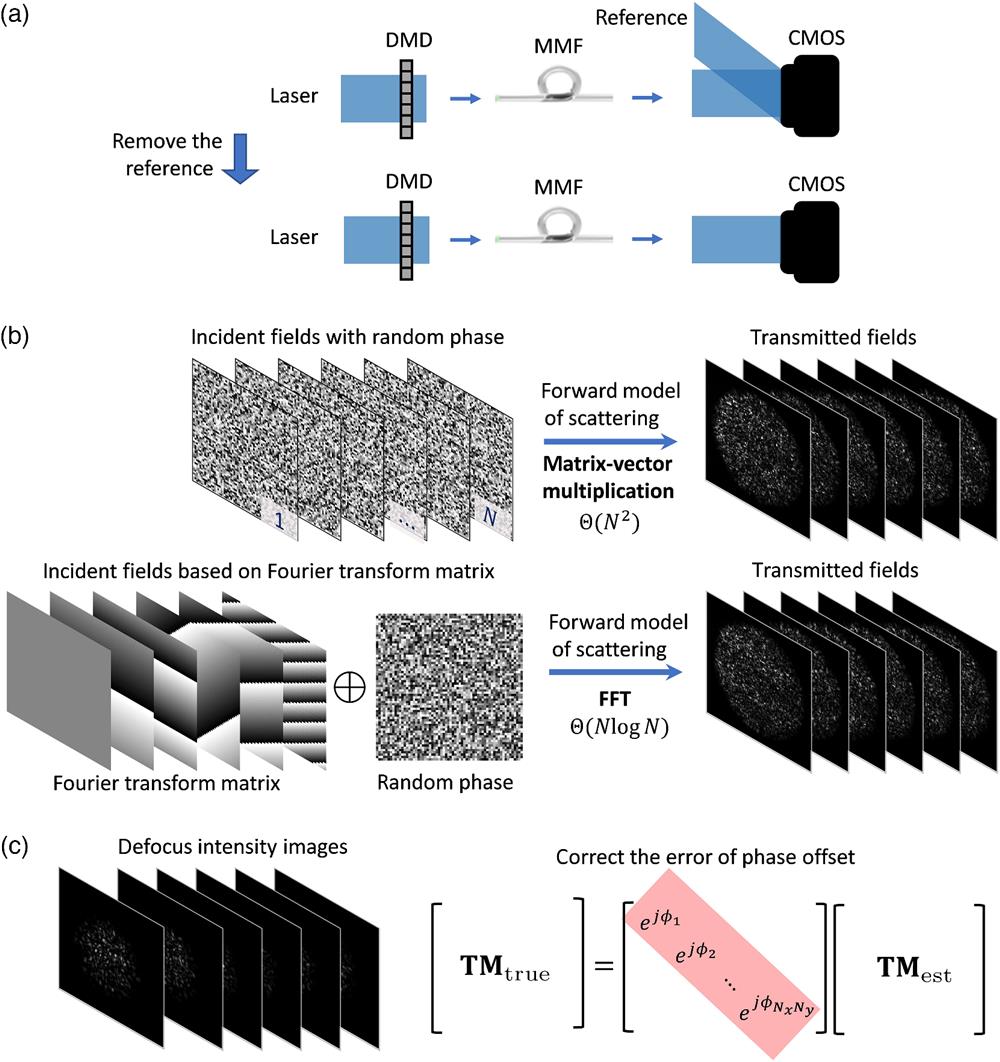
Imaging through multimode fiber (MMF) provides high-resolution imaging through a fiber with cross section down to tens of micrometers. It requires interferometry to measure the full transmission matrix (TM), leading to the drawbacks of complicated experimental setup and phase instability. Reference-less TM retrieval is a promising robust solution that avoids interferometry, since it recovers the TM from intensity-only measurements. However, the long computational time and failure of 3D focusing still limit its application in MMF imaging. We propose an efficient reference-less TM retrieval method by developing a nonlinear optimization algorithm based on fast Fourier transform (FFT). Furthermore, we develop an algorithm to correct the phase offset error of retrieved TM using defocused intensity images and hence achieve 3D focusing. The proposed method is validated by both simulations and experiments. The FFT-based TM retrieval algorithm achieves orders of magnitude of speedup in computational time and recovers 2286 × 8192 TM of a 0.22 NA and 50 μm diameter MMF with 112.9 s by a computer of 32 CPU cores. With the advantages of efficiency and correction of phase offset, our method paves the way for the application of reference-less TM retrieval in not only MMF imaging but also broader applications requiring TM calibration.
transmission matrix retrieval multimode fiber imaging through scattering Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(5): 056007
1 浙江大学 光电科学与工程学院, 浙江 杭州 310027
2 之江实验室 类人感知研究中心, 浙江 杭州 311100
全景内窥成像技术可有效减小体内器官的观察盲区,具有缩短手术时间、降低术中出血风险、改善手术预后、缩短术后恢复时间等多种优点,在微创手术和术前检查中有重要应用价值,是近年来的研究热点。本文从原理和产品应用两个方面对全景内窥成像技术进行了梳理。首先,综述了基于二维和三维成像的各种全景内窥成像技术,阐述了它们各自的实现方式,并分析了其关键指标和性能。其次,对比分析了由全景内窥成像技术衍生出来的胶囊内窥镜、全景结直肠镜等多种不同类型的产品,并展望了全景内窥成像技术的发展趋势和应用前景。
内窥镜 全景成像 3D重建 图像拼接 endoscope panoramic imaging 3D reconstruction image stitching
水下爆炸气泡载荷是造成舰船结构整体损伤的主要原因, 研究水下爆炸气泡动态特性对水中兵器研发和舰船防护等方面至关重要。从水下爆炸气泡脉动的载荷特性出发, 综述了气泡动力学理论、实验和数值模拟三方面的研究进展, 总结气泡非球状坍缩运动过程、气泡与不同结构表面耦合作用以及自由场中多气泡耦合作用等问题的典型研究成果。在现有研究成果的基础上, 提出应建立综合考虑气泡内部因素和水中不同环境因素的气泡运动力学模型; 针对非理想炸药水中爆炸气泡运动特性规律开展更系统的实验研究; 进一步加强近边界条件下多气泡耦合过程的研究工作等建议。
爆炸力学 水下爆炸 气泡 脉动 动态特性 explosive mechanics underwater explosion bubbles pulsation dynamic characteristics
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing System Engineering and Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Photonics Technology for Information, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
Wettability is one of a solid surface’s fundamental physical and chemical properties, which involves a wide range of applications. Femtosecond laser microfabrication has many advantages compared to traditional laser processing. This technology has been successfully applied to control the wettability of material surfaces. This review systematically summarizes the recent progress of femtosecond laser microfabrication in the preparation of various superwetting surfaces. Inspired by nature, the superwettabilities such as superhydrophilicity, superhydrophobicity, superamphiphobicity, underwater superoleophobicity, underwater superaerophobicity, underwater superaerophilicity, slippery liquid-infused porous surface, underwater superpolymphobicity, and supermetalphobicity are obtained on different substrates by the combination of the femtosecond laser-induced micro/nanostructures and appropriate chemical composition. From the perspective of biomimetic preparation, we mainly focus the methods for constructing various kinds of superwetting surfaces by femtosecond laser and the relationship between different laser-induced superwettabilities. The special wettability of solid materials makes the femtosecond laser-functionalized surfaces have many practical applications. Finally, the significant challenges and prospects of this field (femtosecond laser-induced superwettability) are discussed.
Ultrafast Science
2022, 2(1): 9895418
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing System Engineering and Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Photonics Technology for Information, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, People’s Republic of China
2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, People’s Republic of China
Underwater transportation of bubbles and gases has essential applications in manipulating and using gas, but achieving this function at the microscopic level remains a significant challenge. Here, we report a strategy to self-transport gas in water along a laser-induced open superhydrophobic microchannel with a width less than 100 μm. The femtosecond laser can directly write superhydrophobic and underwater superaerophilic microgrooves on the polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) surfaces. In water, the single laser-induced microgroove and water medium generate a hollow microchannel. When the microchannel connects two superhydrophobic regions in water, the gas spontaneously travels from the small region to the large area along this hollow microchannel. Gas self-transportation can be extended to laser-drilled microholes through a thin PTFE sheet, which can even achieve anti-buoyancy unidirectional penetration. The gas can overcome the bubble’s buoyance and spontaneously travel downward. The Laplace pressure difference drives the processes of spontaneous gas transportation and unidirectional bubble passage. We believe the property of gas self-transportation in the femtosecond laser-structured open superhydrophobic and underwater superaerophilic microgrooves/microholes has significant potential applications related to manipulating underwater gas.
femtosecond laser gas transportation superhydrophobicity underwater superaerophilicity water/gas separation International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing
2022, 4(1): 015002
1 云南电网有限责任公司昆明供电局, 云南 昆明 650000
2 重庆大学 电气工程学院, 重庆 400044
基于Pockels效应原理, 分别对交直流混合强电场传感器中的电光传感单元和电场调制机构进行了设计与测试。对电光传感单元结构进行合理设计, 选取并制备相关器件。搭建试验平台, 试验结果表明电光传感单元输入输出具有良好的线性度, 对电场波形的变化具有快速的响应且频率特性良好, 其性能满足测量调制后电场波形的需求。利用电光传感单元和电场调制机构组建传感器, 并测量了交直流混合强电场响应。
交直流电场 电压传感器 Pockels效应 电光传感单元 电场调制 AC and DC electric field voltage sensor Pockels effect electro-optical sensor unit electric field modulation

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Xi’an Jiaotong University, State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing System Engineering, Xi’an, China
2 Xi’an Jiaotong University, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Photonics Technology for Information, Xi’an, China
3 Xi’an Jiaotong University, School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi’an, China
Nanochannel structures with a feature size deeply under the diffraction limit and a high aspect ratio hold huge biomedical significance, which is especially challenging to be realized on hard and brittle materials, such as silica, diamond, and sapphire. By simultaneously depositing the pulse energy on the surface and inside the sample, nanochannels with the smallest feature size of 18 nm (∼1 / 30λ) and more than 200 aspect ratios are achieved inside silica, the mechanism of which can be concluded as the surface assisting material ejection effect. Both the experimental and theoretical results prove that the coaction of the superficial “hot domain” and internal hot domain dominates the generation of the nanochannels, which gives new insights into the laser-material interacting mechanisms and potentially promotes the corresponding application fields.
femtosecond laser direct writing nanochannels spatially shaping surface assisting material ejection Advanced Photonics Nexus
2022, 1(2): 026004





